How to Get Rid of Notbook Lines in Art Using Pixlr
-
Removing bluish lines from a drawing: The rise of the colour channels.
We've all had it that nosotros were happily doodling away in our notebooks, and of a sudden we manage to create a very beautiful cartoon. Only problem is, our notebook is lined-out with blue lines.
At present there are a few tutorials out at that place which'll recommend you to use the contrast tools, or the level tools or even the color-aligning tools. They will give you step-by-stride instructions, giving you lot the reply to all you lot problems in 10 minutes.
I'chiliad not going to do that.
I'll be giving you the most elaborate over convoluted tutorial on removing the blue lines from a drawing you could ever promise to wish for.
Simply first, I'1000 going to talk to y'all near light.
Theory
The fancy physicist name for light is 'electromagnetic radiation', and in that location actually isn't quite annihilation like it in the universe. Depending on the way you look at it, it'southward either made up from tiny particles(similar sand, or more than specifically, atoms), or waves(similar water-waves, or sound).

When looked at in a similar manner to sound, calorie-free too can have a frequency. And with different frequencies the backdrop of light alter:

Like your radio is capable of picking up radio waves and your computer capable of picking upwardly wifi, your eyes are capable of picking upwardly the visible-light frequencies. Humans can pick up the full range of frequencies trough method of our three types of colour cones. These cones are differently sensitive to different colours, the long cone for example is sensitive to cherry-red, yellowish and green, while the middle cone is sensitive to xanthous, green and blue. By measuring the unlike signal-intensities between the info these two cones requite, our encephalon is capable of knowing where a color ranges on the hue range.

On the higher up epitome, Crimson(700nm) would go a small-scale reaction from the Long cone, but no reaction from the Middle and Short cones.
Dark-green(+-550nm) would no reaction from the brusque cones either, but a lot from both Middle and Long cones(most from middle)
Xanthous(+- 620nm) would get an avarage reaction from the Middle cones, a large reaction from the long cones, but none from the Short cones.
Bluish(+-450nm) would get a lot of reaction from the curt cones, but hardly any from the Middle and Long cones.

Specifically, in the example of the purple hues, we really make it upward.

To brand an efficient approximation of the billions of colours humans can meet, monitors and screens made by humans apply carmine, light-green and blue to display images and store images.
And we're going to take advantage of that today.Practical
If you've ever used a radio, you might know that you tin can tune into a specific frequency: A channel. Considering radio and colours are both forms of light, you can tune into a specific frequency of colour likewise. In an image manipulation program(colloqially known as a cartoon plan) specifically, you are looking at the data that tunes into a specific colour channel.
Now, you can apply Photoshop for this, but I'll exist using GIMP. Any prototype manipulation editor that supports aqueduct-manipulation(they usually accept a separate docker for this) will do however. In the case of Krita, which I'll be using in futurity tutorials whenever I tin, the channel-manipulation tools aren't very extensive yet. However, if yous scroll downward, there's some explanation of how to exercise this in Krita.
First off. Nosotros take our paradigm:


It's preferable yous scan information technology in(the quondam image), photographed pictures tend to have a colour distortion(the latter). If y'all do take a motion picture, endeavor doing then during the day when at that place'due south plenty of lite, and try to brand sure the pic is evenly lit.
Secondly, we open up up the picture in our image manipulation programme of selection(in my example, the GIMP).

We detect out where our channels docker is. In my case it was tabbed side by side to the layer docker, and that tends to be it's default spot in many image manipulation programs, if you can't discover it, try to expect under under window->dockable dialogues.

So each of these channels represents a colour, and how much of that colour is nowadays in the finish epitome.

Okay, now the channels docker is a little complicate, only permit's play with it a flake to get to know it. Meet how all three channels are selected and visible?
Ticking on them removes them from the pick, just doesn't make them invisible. Which means that if we deselect the green aqueduct and paint on the prototype with yellow(remember, in light, red+dark-green=yellow).

And if we pigment with white(ruby+green+bluish)

So what's happening now is that only red and blueish can be added to the image because yous only have those two channels selected.
You lot tin encounter it also when you lot hide the green and blue channels.

Okay, so that'due south how the channels docker works. Remove all paint-strokes you made, and select the green channel again.
You may take caught on, what we're going to do is edit these channels to remove the blue lines. Paradoxically, we'll need to edit the ruddy and green channels, because those contain the differences between white(red+dark-green+blue) and blue(only blue).
Deselect the blue channel:

Earlier heading toward the adjacent step, make sure you accept black as foreground colours and white as blackground color. Striking the little black-square over the white square to make sure that is the case..

=>

With merely the red and greenish channel selected, become to EDIT-> Fill with foreground colour(or CTRL+comma; the hotkey). If you lot did that correctly, yous've fabricated the red and green channels completely blackness, and your paradigm should exist black to bluish.


Now right click on the blue-aqueduct, be conscientious you don't select information technology, and click 'channel to selection' or 'add to channel'
Now, with still simply the cherry and green channels selected, get to Edit -> Fill with background colour.(or CTRL+ menses) and then, deselect everything!

Depending on the quality of your movie, you should have lost the blueish lines completely or partially. The partially usually has to do with the color of the lines being slightly different in that part of the picture show.
Considering we made all colour channels exactly alike, our picture is grayscale. (Seriously, you tin can check) So nosotros'll solve those concluding lines with the contrast tools. While you tin utilize the Brightness-dissimilarity for this, information technology's best to utilise the Levels-tool for this.
I prefer the levels tool here considering it's a piddling more intuitive to use. You can also use the curves for this, only it's a little trickier to use. Y'all can find the Levels tool under Colors -> Levels

Then, levels tool. The lilliputian graph that is visible over the upper-bar is an outline of how much of a specific value is used in a picture. In most black and white pictures it ordinarily spikes around the lighter-values.
You lot can play with the lower-bar(output) to see what information technology does, but you probable want to get out it unchanged because our interest lies in the upper-bar(input).

Drag the white pointer to the left, only by the spike in the graph. You should be seeing the leftover-lines gradually disappear. Continue till they're gone. If necessary you can besides drag the black arrow to the correct, to even out the black-lines of your drawing.

Click done and save:

Tada! You've removed the bluish lines from your cartoon.

Now, you may have noticed this little box with "Value" in the Levels-tool and if you lot click it, y'all'll see that you can edit the red-green-blue channels here as well. Which leads us to the following role:
Practical - Function 2:
The faster method.
So, if we return back to our drawing.
Surprising how much we changed huh.
Now we go directly to the Levels-editor.
We set our base-dissimilarity.

We select value and go to each channel to fine tune the dissimilarity there. It should exist slightly college on the red and greenish channels than on the blue.



Yous will really need to fiddle and tweak with these settings to go what you want, only eventually, it should exist possible to get this:

And then, how to do this in Krita?
Well, Krita doesn't accept the ability to add a colour channel to a selection, nor does it accept the ability to edit them in the levels tool.
Still, it does in the curves tool, which is under Filters -> Adjustment -> Color Adjustment Curves.

The steepness of the curve is the contrast. You'll have to figure it out for each aqueduct, just like with levels.
Now, to rid the last bit of discolouration, go to Filters -> Adjustment -> Desaturnate.

Done!
Manner #iii: More channels, more fun!
And so, while initially the Channels were named as such because they stand for a frequency, programmers take since hijacked the term for anything using a greyscale motion picture to store data, amid which, a term you may accept heard of: the alpha channel. Or rather, the transparency.
Supposedly, the alpha aqueduct is named as such because it was represented every bit the alphabetic character α in the original equations for calculating an epitome with an blastoff aqueduct over another image. Because this blastoff tin can be represented every bit a greyscale image, it was decided to encode it similarly to the color channels. And thus the blurring of the term 'Channel' bagan.
There'south a filter in both Gimp and Krita that allows you lot to brand ane color in a picture completely transparent. We're going to use this filter in a method to set the color we option to be the only one that isn't transparent.
For this one I increased the contrast, because for my lineart it's of import the blackness was fully blackness. Even so, if you are doing the same to a pencil piece, you don't have to do this, the method will work without :)

We'll be using the colour-to-alpha for this and the layers docker for this, you can find the windows->dockable dialogues. In GIMP this can be constitute under the Colors card, in Krita under Filters->Colors->Color to alpha.
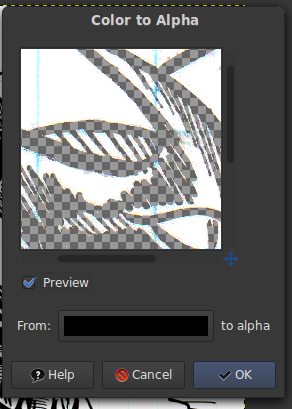
By default, colour to alpha is set up to white, click the white bar to get a colour-selector and set information technology to black.

This should be the event.
Now, we're going to brand a new layer and fill up information technology with our foreground colour(set the foreground colour to black.) You can add layers on the layer docker or under layers-> new layer.

You should now have a full black layer.
Correct click on the lower-layer, the original picture. Below in the rightclick card, yous should come across in Gimp "Alpha to Selection" and in Krita "Select opaque". Click that.
Now select the upper layer, and striking the delete primal. Hibernate the lower layer.

Tada! It'south all transparent now.
Conclusion and afterthoughts:
I hope you learned something from this tutorial, even though information technology starts at a completely different identify than you end up in. This is not the last tutorial I'll write about colours channels, or fifty-fifty RGB itself, and I hope this tutorial is a good grooming for those.
In the concurrently, I promise you lot can put these convoluted but computer-scientifically correct ways of removing blueish lines to skilful apply.
Next fourth dimension: Flat-colouring and the layer system.
Sources:
Physics behind light: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light and every modern schoolbook on physics. Likewise http://www.youtube.com/spotter?v=Q_h4IoPJXZw and http://www.youtube.com/lookout man?v=DfPeprQ7oGc
Frequencies light: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:EM_spectrum.svg
Pinkish is an imaginary color: http://www.youtube.com/watch?five=S9dqJRyk0YM
Definition aqueduct: http://www.merriam-webster.com/lexicon/channel (f : a band of frequencies of sufficient width for a single radio or television advice ) and http://dictionary.reference.com/scan/channel ( "a ring of radio frequencies assigned for a particular purpose, esp the broadcasting of a television point")
Dog's vision: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dog, http://dog-vision.com/
Colorblindness: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_blindness
Tetrachomats and human lenses blocking UV-light: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetrachromacy
Vision in collywobbles: http://www.butterflyzone.org/butterfly-manufactures/butterfly-uv-vision.shtml
Mantis shrimp vision: http://theconversation.com/mantis-shrimp-have-the-worlds-all-time-eyes-but-why-17577 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mantis_shrimp
Significant Alpha-channel: http://world wide web.peachpit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=1617518&seqNum=6
EDIT(November 29 2013): I had to change a bit in the Human colour vision department due to what I found out while researching colour theory. The section is now less cohesive, my apologies.
-
 colorbandiits liked this
colorbandiits liked this -
random-art liked this
- Show more notesLoading...
-
witcherpothumlect.blogspot.com
Source: https://theratutorial.tumblr.com/post/65808232987/removing-blue-lines-from-a-drawing-the-rise-of
0 Response to "How to Get Rid of Notbook Lines in Art Using Pixlr"
Post a Comment